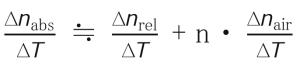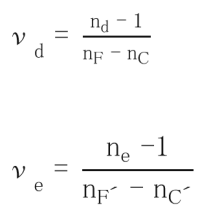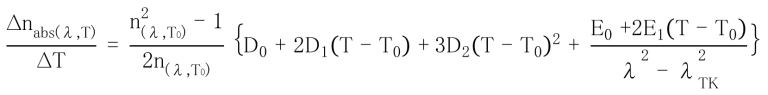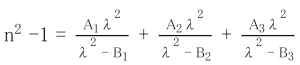6 Other Properties
6.1 Bubble & Inclusion
It is most desirable to manufacture bubble-free optical glass, but the existence of bubbles to some extent is inevitable. Bubbles in optical glass vary in size and number from one glass to another due to the many different compositions and production methods. The classification of bubble content is established by specifying in mm2 the total bubble cross sections existing in 100ml of glass volume. Inclusions such as small stones or crystals are treated as bubbles. The bubble classes are shown in Table 1. The classification includes all bubbles and inclusions measuring larger than 0.03mm.
Table 1
| Class | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
The total cross section of bubbles (mm2 /100cm3 ) | <0.03 | > 0.03 <0.1 | > 0.1 <0.25 | > 0.25 0.5 | > 0.5 |
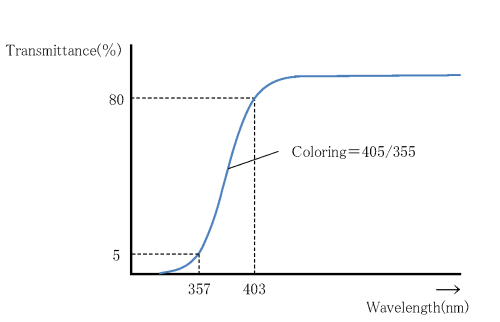
6.2 Coloring
Internal transmittance ( t ) of optical glass is listed for each glass type. To express absorption, a column labeled “Coloring” is provided in the catalog page. Coloring can be determined by measuring spectral transmission including reflection losses with 10 mm thick test pieces. The wavelengths corresponding to 80% transmission and 5% transmission are given. For glass types of S-TIH 53 , PBH 71 and LAH78 reflection losses are so large that we used the wavelength corresponding to 70% in place of 80%.
6.3 Specific Gravity d)
Specific gravity is the density value of well-annealed glass referenced against pure water at 4 °C, with the value shown to the second decimal place.